This post will explain how to interpret the ratings assigned to insurers that underwrite legal malpractice insurance.
Legal Malpractice Insurance Insurer Ratings Explained
When attorneys receive quotes from a given insurer, the insurer is often described as ‘A’-rated, ‘B’-rated, etc. They instinctively understand that a higher rating is better, but what exactly is being rated?
An insurer’s ratings are an indicator of its financial strength and claims-paying ability, i.e., its ability to honor its contractual obligations to policyholders. So, the higher an insurer’s rating, the stronger it is financially, and thus the more likely it is, to be able to pay claims.
An insurer’s rating, is based on an analysis of its business profile, balance sheet, operating performance, and how it compares to its competitors, as well as the macroeconomic outlook, i.e., inflation, interest rates, economic (GDP) growth, etc. However, the analysis and assumptions that underlie a particular rating, may be incorrect, so it’s not a guarantee of future performance.
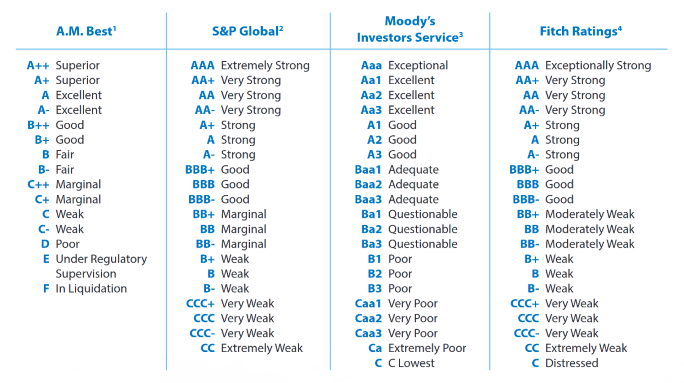
There are four main rating agencies: A.M. Best, Standard & Poor’s, Moody’s, and Fitch, each of which uses its own proprietary scale to rate insurers.
Retirement Plan Advisors provides this summary of the the main rating agencies’ rating scales:
However, A.M. Best’s ratings are the most widely used, to the point that insurance industry professionals ask, colloquially, “what is (a given insurer’s) Best rating?”
In Guide to Best’s Financial Strength Ratings, A.M. Best states that its Financial Strength Rating (FSR) of a given insurer, “is an independent opinion of an insurer’s financial strength and ability to meet its ongoing insurance policy and contract obligations. (It) does not address any other risk…including, an insurer’s claims-payment policies or procedures; the ability of the insurer to dispute or deny claims payment on grounds of misrepresentation or fraud; or any specific liability contractually borne by the policy or contract holder.”
Here’s Best’s explanation of its rating categories:
|
Best’s Financial Strength Rating (FSR) Scale |
|||
|
Rating Categories |
Rating Symbols |
Rating Notches* |
Category Definitions |
|
Superior |
A+ |
A++ |
Assigned to insurance companies that have, in our opinion, a superior ability to meet their ongoing insurance obligations. |
|
Excellent |
A |
A- |
Assigned to insurance companies that have, in our opinion, an excellent ability to meet their ongoing insurance obligations. |
|
Good |
B+ |
B++ |
Assigned to insurance companies that have, in our opinion, a good ability to meet their ongoing insurance obligations. |
|
Fair |
B |
B- |
Assigned to insurance companies that have, in our opinion, a fair ability to meet their ongoing insurance obligations. Financial strength is vulnerable to adverse changes in underwriting and economic conditions. |
|
Marginal |
C+ |
C++ |
Assigned to insurance companies that have, in our opinion, a marginal ability to meet their ongoing insurance obligations. Financial strength is vulnerable to adverse changes in underwriting and economic conditions. |
|
Weak |
C |
C- |
Assigned to insurance companies that have, in our opinion, a weak ability to meet their ongoing insurance obligations. Financial strength is very vulnerable to adverse changes in underwriting and economic conditions. |
|
Poor |
D |
– |
Assigned to insurance companies that have, in our opinion, a poor ability to meet their ongoing insurance obligations. Financial strength is extremely vulnerable to adverse changes in underwriting and economic conditions. |
Legal Malpractice Insurance Insurer Ratings – How to Use Them in Buying a Policy
Attorneys should never accept a quote from an insurer that has less than an ‘A’-rating.
The risk of an insurer becoming insolvent, and thus being unable to pay its claims, is significantly higher among insurers rated ‘B’ or lower, than it is among those rated ‘A’, so obtaining coverage from such a low-rated insurer, adds an element of risk that more than offsets any savings you may obtain.
In fact, pricing policies below market, usually results in financial losses that increase an insurer’s insolvency risk, which in turn results in it receiving a low rating.
Further, the legal malpractice insurance market is large and intensely competitive, with dozens of ‘A’-rated insurers, actively seeking to underwrite policies.
With careful shopping, attorneys should be able to obtain a quote from a top-rated, nationally-known insurer, like CNA, AIG, Travelers, etc., that’s competitive with any low-rated insurer’s quote, and carries much lower insolvency risk.